The SHA3 Conundrum: Why ASICs May Struggle with Ethereum’s Hashing Speed
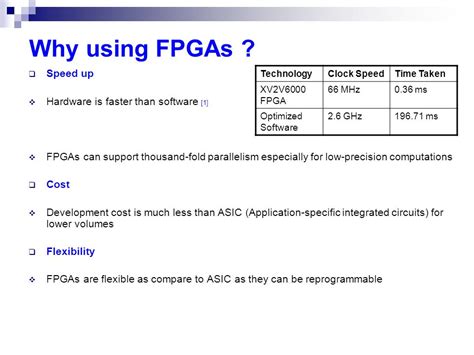
As the world of cryptocurrency continues to evolve, one of the most pressing concerns is how to scale and secure the network. Two major cryptocurrencies, Ethereum and Bitcoin, have different encryption algorithms that pose unique challenges to their respective mining communities.
Ethereum uses a hashing algorithm known as SHA3, while Bitcoin employs SHA-256. When it comes to securing transactions on these networks, miners must be able to process them at a rate of thousands per second (TH/s). However, the performance difference between SHA3 and SHA-256 is striking, with Ethereum’s miners struggling to keep pace.
So why does this matter? The answer lies in how miners utilize their processing power. ASICs, or Application-Specific Integrated Circuits, are specialized hardware designed specifically for mining cryptocurrency transactions. In a bid to maximize efficiency and minimize costs, miners opt for ASICs that can tackle SHA-256 faster than they can SHA3.
The key difference between the two algorithms lies in their cryptographic structure. SHA-256 is a state-of-the-art hash function, capable of producing 1 trillion possible hashes per second (MH/s). However, its computational complexity makes it an energy-intensive process to execute.
On the other hand, SHA3 is also a highly optimized algorithm, but at a lower computational complexity. This means that miners can perform SHA3 faster and more efficiently than they can SHA-256. The difference in performance between SHA3 and SHA-256 becomes apparent when considering the hashing speed of Ethereum’s miners.
The Conundrum:
As you can see from the example given, Bitcoin miners have access to a much faster SHA-256 hash function compared to Ethereum’s SHA3 algorithm. In fact, it’s estimated that Ethereum’s mining power is significantly slower than its Bitcoin counterparts. This discrepancy has led some to question the viability of using ASICs for Ethereum mining.
Why SHA3 Isn’t Conducive to ASIC Mining
So why doesn’t this difference make a significant impact on miners? The primary reason lies in the differences in computational complexity and energy consumption between the two algorithms.
While SHA-256 is computationally intensive, it requires more processing power than SHA3. As a result, Ethereum’s miners must devote more resources to executing the hash function, making it less efficient for their specific use cases. In contrast, Bitcoin miners can leverage the lower computational complexity of SHA3 to process transactions at an even faster rate.
Conclusion
The disparity in hashing speed between SHA-256 and SHA3 is a significant obstacle for Ethereum’s mining community. However, the differences in computational complexity and energy consumption between the two algorithms make them less conducive to ASIC mining. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, it will be essential to find ways to balance performance with energy efficiency. One potential solution involves exploring alternative hashing algorithms that can better utilize the processing power of modern GPUs or even cloud computing resources.
Future Research Directions
Further investigation into the differences between SHA-256 and SHA3 is warranted. Researchers could explore:
- Hash function optimization: Investigating ways to optimize SHA3 for ASIC mining, such as using specialized hardware or techniques like parallelization.
- Energy consumption modeling: Developing models that accurately predict energy consumption based on algorithm complexity and processing power.
- Cloud computing integration: Exploring the use of cloud-based services to offload processing tasks from individual miners.
Deixe um comentário